Introduction:
Monitor scaling is the adjustment of how content appears on your screen. It ensures that icons, text, images, and apps are readable and usable on displays of varying resolutions. Without scaling, high-resolution monitors like 4K or 8K would show text and icons so small that you’d need to squint or lean in close to see them.
Monitor scaling ensures text, icons, and apps stay clear on high-res screens like 4K. It adjusts size without losing clarity, improving usability for work, gaming, and design. Proper scaling also reduces eye strain for comfortable viewing. It also helps maintain consistent visuals across multiple monitors.
Scaling acts like a digital magnifier, enlarging or reducing visual elements so they’re comfortable to view without sacrificing too much clarity.
In This Article, we discuss “Monitor Scaling.”
Why Scaling Matters in Today’s World:
Scaling is no longer optional—it’s essential. We live in an era where people use multiple monitors, ultra-wide displays, and devices with wildly varying resolutions. Without scaling, a 4K laptop screen would display apps so tiny they’d be practically unusable.
Likewise, professionals working with detailed graphics or large spreadsheets would struggle without the flexibility scaling provides. In short, scaling keeps modern technology usable for everyone, regardless of eyesight or monitor type.
The Evolution of Display Resolutions:
From 480p to 8K Displays:
Back in the CRT era, most users were comfortable with 480p or 720p resolutions. Everything looked bigger, even if it wasn’t crystal clear. Then came 1080p, which quickly became the standard for both work and entertainment.
Today, 4K is the norm for professionals and gamers, while 8K displays are slowly entering the market. The higher the resolution, the smaller things appear. This shift has made scaling more critical than ever.
How Resolution Impacts Scaling:
Resolution determines how many pixels fit into your screen. A 15-inch 1080p laptop and a 15-inch 4K laptop have the same size screen, but the 4K display crams in four times the number of pixels.
Without scaling, everything on the 4K laptop would appear four times smaller. That’s where scaling steps in, enlarging digital elements while keeping them sharp and readable.
How Monitor Scaling Works:

The Role of Pixels:
Pixels are the building blocks of your screen. Scaling manipulates how these pixels are used to represent content. At 100% scaling, one app pixel equals one monitor pixel.
At 200% scaling, each app pixel takes up four monitor pixels, making it twice as large but still sharp. This balance between size and clarity is what makes scaling so useful.
Operating System Scaling vs. Application Scaling:
Scaling can happen at two levels: system-wide and app-specific. Your operating system provides the main scaling settings, but individual applications may or may not support them. Modern apps usually adapt well, but older software sometimes struggles, leading to blurry text or squashed layouts.
GPU’s Contribution to Scaling:
Your GPU (graphics processing unit) also has a say in scaling. It renders images, games, and videos, applying scaling techniques that improve clarity.
With the rise of AI-driven upscaling, GPUs don’t just enlarge images—they enhance them, making them appear sharper than their original resolution would suggest.
Types of Monitor Scaling:
DPI (Dots Per Inch) Scaling:
Why DPI Scaling is Crucial:
DPI scaling determines how large things appear on your screen. It’s especially vital for people using high-resolution displays, as it ensures text and icons remain legible without squinting.
Common DPI Settings and Their Uses
The DPI values of 100%, 125%, 150%, and 200% are frequently used. For a 1080p display, 100% is standard. For a 4K display, 150% or 200% is more comfortable. It’s all about finding a balance between readability and usable workspace.
Aspect Ratio Scaling:
4:3, 16:9, and 21:9 Explained:
Your content’s proportions are maintained by aspect ratio scaling. To prevent distortion, a vintage 4:3 video on a contemporary 16:9 screen will be stretched, letterboxed, or appropriately scaled.
Even more complication is added by ultra-wide monitors (21:9 or 32:9), which call for careful scaling in order to display programs and videos without stretching them.
Problems with Mismatched Aspect Ratios:
If scaling isn’t applied, the content may look distorted. Circles might appear as ovals, and videos may have black bars. For gamers, mismatched aspect ratios can ruin immersion, while for designers, they can ruin accuracy.
Resolution Scaling:
Native Resolution vs. Scaled Resolution:
Native resolution is your monitor’s optimal setting. Running at lower resolutions may help performance, but it often sacrifices sharpness. Resolution scaling bridges the gap by allowing lower-resolution content to display smoothly on higher-resolution screens.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Resolution Scaling:
The benefit is obvious—better performance without losing usability. The drawback is that scaling can sometimes blur content, especially text. This is why native resolution is usually preferred for productivity tasks, while resolution scaling is common in gaming.
Custom Scaling:
When to Use Custom Scaling:
Sometimes, the preset scaling options don’t work for you. If 125% feels too small and 150% feels too big, custom scaling lets you pick something in between—say, 135%.
Risks of Over-Scaling:
Custom scaling comes with risks. Some apps may not adapt correctly, leading to overlapping windows, menus that don’t fit, or misaligned icons. Over-scaling can also cause performance hiccups.
Monitor Scaling in Different Systems:
Scaling on Windows:
How Windows Handles Scaling:
Windows offers per-monitor DPI scaling, allowing different scaling settings for each monitor. This is handy if you’re using a 4K screen alongside a 1080p one.
Common Issues and Fixes:
Unfortunately, Windows apps don’t always handle scaling perfectly. You may encounter blurry text or oversized toolbars. Thankfully, adjusting compatibility settings or updating apps usually solves these problems.
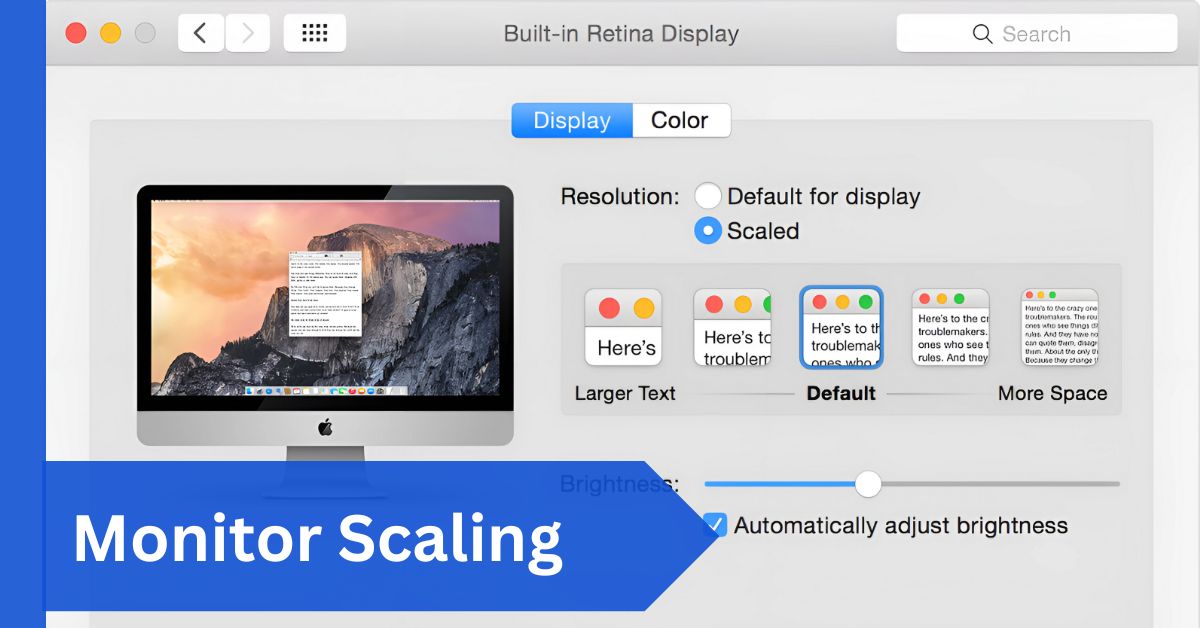
Scaling on macOS:
Retina Displays and Scaling:
Apple’s Retina display technology is a textbook example of good scaling. macOS scales content seamlessly, ensuring text and images look sharp without you noticing any trade-offs.
Advantages of Apple’s Approach:
Because Apple controls both the hardware and software, macOS avoids many of the scaling issues that plague Windows and Linux. This makes it the smoothest experience for users who value consistency.
Scaling on Linux:
The Flexibility of Linux Scaling:
Linux stands out for its fractional scaling, which lets you scale at percentages like 110% or 135%, offering more precise control.
Challenges Faced by Linux Users:
The downside is inconsistency. Different desktop environments (like GNOME or KDE) handle scaling differently. Apps may not always follow the scaling rules, leading to a patchwork experience.
Monitor Scaling in Gaming:

Why Scaling is Critical for Gamers:
Scaling can make or break a gaming experience. Higher resolutions look amazing but can drain performance. Scaling gives gamers a middle ground—smooth gameplay with acceptable visuals.
FPS Impact:
Lowering resolution and letting the GPU upscale frames often boosts frame rates dramatically. For gamers who compete, where every millisecond matters, this is essential.
Visual Quality Trade-offs:
However, casual gamers who value immersion may find the visual trade-offs too distracting. Scaling introduces blur or artifacts if not handled well.
GPU Upscaling Technologies:
NVIDIA DLSS:
DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) is one of the most advanced upscaling techniques, using AI to rebuild images at higher resolutions than they were rendered.
AMD FSR:
FSR (FidelityFX Super Resolution) offers a more accessible solution. It doesn’t require proprietary hardware, making it available to a broader audience.
Intel XeSS:
In direct competition with NVIDIA and AMD, Intel’s XeSS introduces AI upscaling to Intel GPUs. While newer, it shows promise in supported games.
Competitive vs. Casual Gaming Scaling Needs:
Competitive gamers prioritize FPS over visuals, often opting for lower resolutions. Casual gamers prefer sharper, more immersive visuals, even if it means fewer frames per second. Scaling settings let both groups tailor the experience to their preferences.
Real-World Applications of Monitor Scaling:
Productivity and Multitasking:
Scaling lets professionals work comfortably across multiple applications. On a 4K monitor, for example, scaling ensures text is readable while still giving space to open several windows at once.
Graphic Design and Video Editing:
Designers and editors rely on accurate scaling for precision. An element that is not scaled correctly could disrupt the entire design. What you see is what you get when scaling is done correctly.
Accessibility for Users with Visual Impairments:
Scaling makes digital devices accessible to people with vision challenges. Larger text, bigger icons, and better readability can make the difference between independence and struggle.
Everyday Office Use:
For office workers, scaling ensures that working long hours doesn’t lead to eye strain. From spreadsheets to presentations, scaling makes everyday tasks more comfortable.
Challenges and Issues with Monitor Scaling:
Blurry Text and Images:
Improper scaling often leads to blurry text, especially in apps that weren’t designed with high-DPI displays in mind.
App Compatibility Problems:
Older applications may not handle scaling gracefully. This results in squashed layouts or buttons that are too small to click comfortably.
Scaling Differences Across Multiple Monitors:
If you’re using a 4K monitor alongside a 1080p monitor, you may find scaling inconsistent between the two. Text may look sharp on one and blurry on the other.
Performance Drops:
High levels of scaling, especially in gaming, can push your GPU harder, leading to performance drops. Striking the right balance is key.
Future of Monitor Scaling:
AI-Powered Scaling:
AI will play a bigger role in scaling. Just as DLSS and FSR revolutionized gaming, similar AI-driven scaling may improve productivity apps, streaming, and even video calls.
Hardware Innovations:
Future monitors may come with built-in chips dedicated to scaling, removing the strain from the GPU, and delivering sharper results.
Standardization Across Platforms:
More uniform scaling across devices is probably in store. A uniform standard might result in fewer incompatibilities and a more seamless user experience.
Conclusion:
Monitor scaling is the unsung hero of modern computing. It ensures that high-resolution displays remain usable, comfortable, and efficient. Whether you’re a gamer chasing higher FPS, a designer working on pixel-perfect visuals, or someone who just wants to read emails without squinting, scaling matters.
It bridges the gap between clarity and usability, making our digital experiences smoother and more accessible. And as technology evolves, scaling will only get smarter, sharper, and more seamless.
FAQs:
1. For 4K monitors, what is the ideal scaling setting?
150% scaling is ideal for most 27–32-inch 4K monitors, offering readability without wasting too much screen space. This balance ensures text and icons remain crisp while maximizing your display’s potential.
2. Does scaling affect gaming performance?
Yes. Lower resolutions with GPU upscaling often improve performance, but may reduce image clarity. Gamers usually experiment with settings to find the sweet spot between smooth play and sharp visuals.
3. Why does text look blurry on my screen?
Blurry text happens when apps don’t support scaling properly. Compatibility settings usually fix the issue. Updating your graphics driver can also help improve sharpness and compatibility.
4. Is custom scaling safe to use?
It’s safe but can cause layout glitches. Always test settings before settling on them. If problems occur, you can easily revert to default scaling without harming your system.
5. How will scaling improve in the future?
Future scaling will likely rely on AI, making it adaptive and sharper across all apps and devices. This means displays will automatically adjust for clarity without manual tweaking.